|
|
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, three giants stand tall – Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure. Each of these cloud providers offers a vast array of services, catering to the diverse needs of businesses and individuals alike.
When it comes to deciding which public cloud provider to use, there are several factors to consider. In this blog post, we will delve into the history of these cloud providers, explore the pros and cons they bring to the table, and highlight some of the prominent companies leveraging their services.
Table of Contents
Brief History of the Top Cloud Providers
History of AWS
The granddaddy of the cloud, Amazon revolutionized the game with its early launch and diverse service offerings. AWS was the first major cloud provider, launched in 2006 and is often considered the pioneer of cloud computing. AWS initially started as a way to provide scalable computing power, it has since expanded to offer a comprehensive suite of services.
AWS pioneered the Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) model and continues to lead in market share today. AWS has played a significant role in shaping the cloud industry and is renowned for its reliability and extensive global infrastructure.
History of GCP
Born from Google’s tech prowess, GCP leverages powerful AI and analytics tools to cater to data-driven enterprises. Launched in 2008 initially as App Engine, focusing on Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS). Expanded to full cloud platform in 2016.
Known for its innovation and expertise in data analytics and machine learning, GCP has gained popularity for hosting data-intensive applications.
History of Azure
Microsoft’s cloud offering integrates seamlessly with its existing software suite, ideal for Windows-centric businesses. Launched in 2010 to compete with AWS. Azure has grown quickly to become the second largest cloud provider.
Azure has positioned itself as a comprehensive cloud solution, seamlessly integrating with Microsoft’s other products and services.
Comparative Summary of Cloud Services
A quick glance from Q2-2023 shows AWS is still on the top of the clouds.
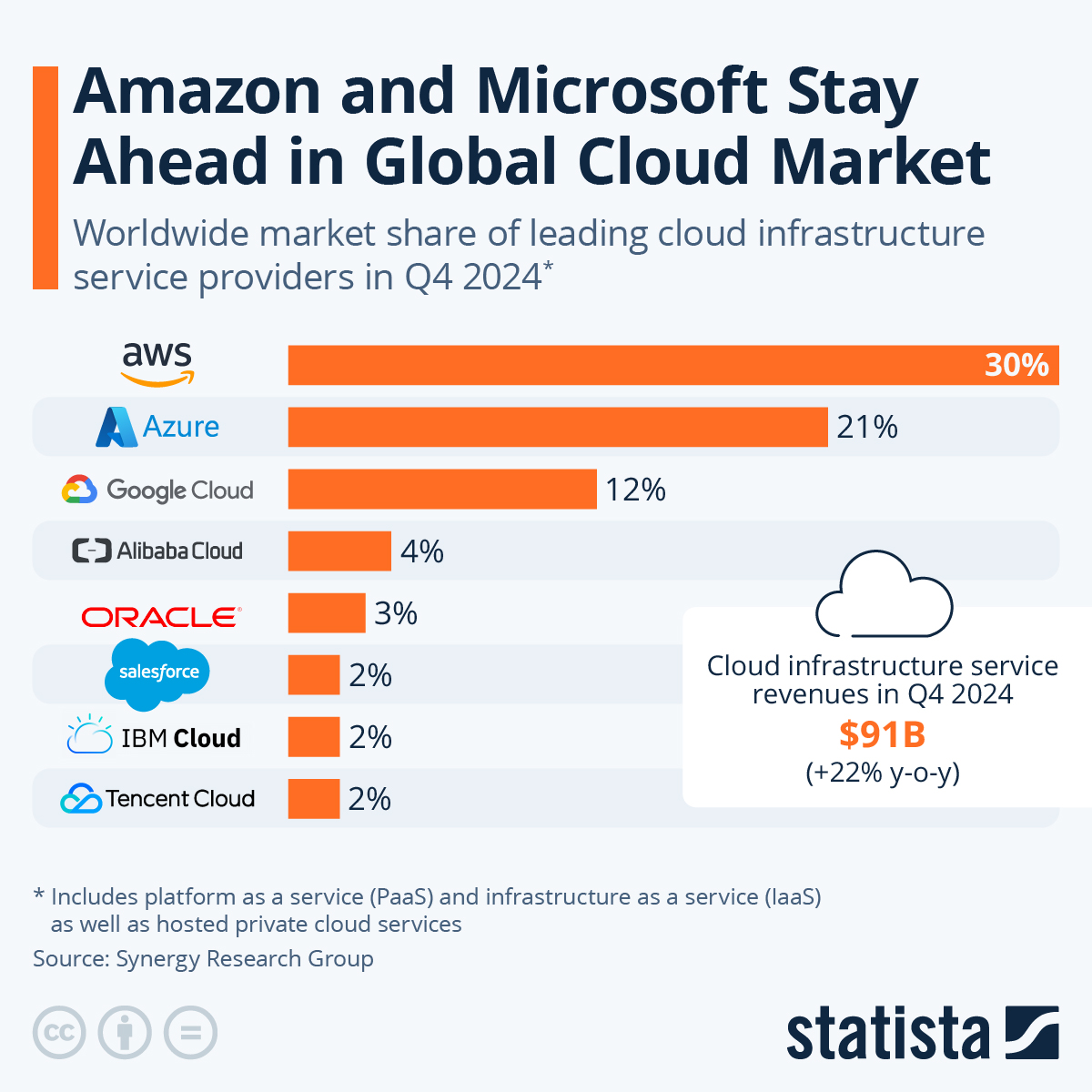
Here’s a quick comparative summary of cloud computing services offered by AWS, GCP, and Azure:
| Category | AWS | GCP | Azure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compute Services | EC2, Lambda, ECS | Compute Engine, Cloud Functions, GKE | Virtual Machines, Azure Functions, AKS |
| Storage Services | S3, EBS, Glacier | Cloud Storage, Persistent Disks, Nearline | Blob Storage, Managed Disks, Archive Storage |
| Database Services | RDS, DynamoDB, Aurora | Cloud SQL, Firestore, Bigtable | Azure SQL Database, Cosmos DB, MySQL/PostgreSQL |
| Networking Services | VPC, Route 53, Direct Connect | VPC, Cloud DNS, Cloud Interconnect | Virtual Network, Azure DNS, ExpressRoute |
| ML and AI Services | SageMaker, Comprehend, Rekognition | AI Platform, Natural Language API, Vision AI | Azure Machine Learning, Text Analytics, Computer Vision |
| Identity and Access Management | IAM, Cognito, KMS | IAM, Cloud Identity-Aware Proxy, KMS | Azure Active Directory, AD B2C, Key Vault |
| DevOps and Developer Tools | CodePipeline, CodeBuild, CloudFormation | Cloud Build, Cloud Source Repositories, Deployment Manager | Azure DevOps, Azure Repos, Azure Resource Manager |
This tabular format provides a concise overview of the diverse services offered by each cloud provider across various categories. It can be a helpful reference for businesses seeking to compare and choose the most suitable cloud platform based on their specific needs.
How do I choose which cloud provider is best for me?
Choosing the right cloud provider for your needs requires careful consideration of various factors. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision:
- Define Your Requirements: Start by identifying your specific business requirements. Consider factors such as the nature of your applications, data storage needs, scalability requirements, and budget constraints.
- Service Offerings: Compare the services offered by each cloud provider. Look into compute, storage, database, networking, machine learning, and other specialized services. Choose a provider that aligns with the services essential for your applications.
- Performance and Reliability: Evaluate the performance and reliability of each cloud provider. Consider factors like uptime, service-level agreements (SLAs), and the global infrastructure. Choose a provider with a strong track record in providing reliable services.
- Cost Considerations: Assess the pricing models of each cloud provider. Consider your budget and analyze the cost structures, including compute, storage, and data transfer costs. Take into account any hidden fees and choose a provider that offers transparent pricing aligned with your financial considerations.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Consider the scalability and flexibility of each cloud platform. Determine how easily you can scale resources up or down based on demand. Ensure that the chosen provider can accommodate your future growth and evolving business needs.
- Integration and Ecosystem: Evaluate how well each cloud provider integrates with your existing systems and tools. If your organization already uses specific technologies or software, choose a cloud provider that seamlessly integrates with your current ecosystem.
- Security and Compliance: Examine the security features and compliance certifications of each cloud provider. Consider your industry’s regulatory requirements and ensure that the chosen provider adheres to necessary security standards.
- Support and Documentation: Assess the level of support and documentation provided by each cloud provider. Look for a provider with robust documentation, a responsive support system, and a community that can help you troubleshoot issues.
- Geographic Presence: Consider the geographic presence of each cloud provider. Choose one with data centers in regions that align with your target audience or comply with data residency regulations.
- User-Friendly Interface: Evaluate the user interface and ease of use of each cloud platform. Consider your team’s expertise and familiarity with the provider’s tools. Choose a platform that aligns with your team’s skills and preferences.
- Community and Ecosystem: Consider the community support and ecosystem around each cloud provider. A vibrant community can be beneficial for troubleshooting, sharing best practices, and leveraging third-party tools and integrations.
- Trial Periods and Free Tiers: Many cloud providers offer trial periods or free tiers. Take advantage of these to test the services, evaluate performance, and assess the ease of use before making a long-term commitment.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make a well-informed decision on which cloud service provider is best suited for your specific requirements and business objectives. It’s often beneficial to start with a pilot project or a small-scale deployment to evaluate the chosen cloud platform in a real-world scenario before fully committing.
Overall Comparative Summary
Here’s the information presented in a tabular format for better clarity:
| Aspect | AWS | GCP | Azure |
|---|---|---|---|
| History | Launched in 2006, a pioneer in cloud computing. | Introduced in 2008, evolved from Google’s internal infrastructure. | Debuted in 2010, building upon Microsoft’s existing enterprise offerings. |
| Service Catalog | Extensive, diverse range of services. | Strong emphasis on data analytics, ML, and AI. | Comprehensive cloud solution with seamless integration. |
| Global Presence | Data centers in multiple regions, extensive global infrastructure. | Smaller market share, limited availability in some regions. | Global reach with a broad network of data centers. |
| Ecosystem | Established customer base, robust ecosystem. | Known for innovation, particularly in data-intensive applications. | Seamless integration with Microsoft’s products. |
| Pricing | Complex pricing structure, potentially challenging for beginners. | Transparent and straightforward pricing model. | Learning curve for users unfamiliar with Microsoft’s pricing. |
| Innovation | Constantly evolving and introducing new services. | Cutting-edge technology, especially in data analytics and ML. | Focus on enterprise-friendly solutions and hybrid cloud. |
| Sustainability | N/A | Committed to using renewable energy sources. | N/A |
| Market Share | Largest market share among cloud providers. | Smaller market share compared to AWS and Azure. | Significant market presence. |
| Customer Base | Netflix, Airbnb, Lyft, Slack, etc. | Spotify, Snapchat, PayPal, Etsy, etc. | BMW, Adobe, HP, Johnson Controls, etc. |
| Integration | Varied, may require expertise in navigating a vast number of services. | May have a learning curve, but well-integrated with Google’s ecosystem. | Seamless integration with Microsoft’s suite of products. |
This tabular format provides a quick overview of the key aspects of AWS, GCP, and Azure, making it easier to compare their strengths and weaknesses.
Final Thoughts
Selecting the right cloud provider involves a careful evaluation of individual business requirements, technical expertise, and budget considerations. AWS, GCP, and Azure each bring their own strengths to the table, and the choice ultimately depends on the specific needs and priorities of your organization.
As technology continues to advance, staying informed about the latest developments in cloud services will be crucial for making informed decisions and navigating the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing.
Further Reading:
Beginners Guide To Cloud Certifications.
Is getting a cloud certification worth it? Examining the Pros and Cons.

